Hurricanes And Climate Change: Boy Is This Science Not Settled!
Posted on 3 September 2010 by gpwayne
The current research into the effects of climate change on tropical storms demonstrates not only the virtues and transparency of the scientific method at work, but rebuts the frequent suggestion that scientists fit their findings to a pre-determined agenda in support of climate change. In the case of storm frequency, there is no consensus and reputable scientists have two diametrically opposed theories about increasing frequencies of such events.
The background to these enquiries stems from a simple observation: extra heat in the air or the oceans is a form of energy, and storms are driven by such energy. What we do not know is whether we might see more storms as a result of extra energy or, as other researchers believe, the storms may grow more intense, but the number might actually diminish.
What do the records show? According to the Pew Centre, “Globally, there is an average of about 90 tropical storms a year”. The IPCC AR4 report (2007) says regarding global tropical storms: "There is no clear trend in the annual numbers [i.e. frequency] of tropical cyclones."
But this graph, also from the Pew Centre, shows a 40% increase in North Atlantic tropical storms over the historic maximum of the mid-1950, which at the time was considered extreme:
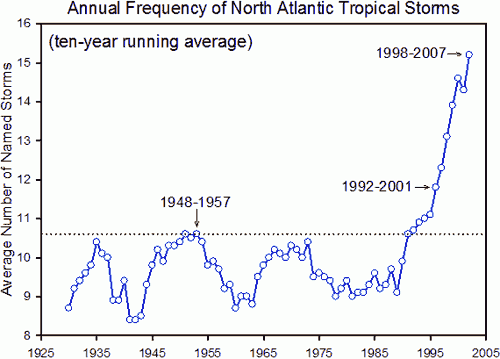
But while the numbers are not contested, their significance most certainly is. Another study considered how this information was being collected, and research suggested that the increase in reported storms was due to improved monitoring rather than more storms actually taking place.
And to cap it off, two recent peer-reviewed studies completely contradict each other. One paper predicts considerably more storms due to global warming. Another paper suggests the exact opposite – that there will be fewer storms in the future.
What can we conclude from these studies? About hurricane frequency – not much; the jury is out, as they say. About climate change, we can say that these differing approaches are the very stuff of good science, and the science clearly isn’t settled! It is also obvious that researchers are not shying away from refuting associations with climate change, so we can assume they don’t think their funding or salaries are jeopardised by research they believe fails to support the case for AGW. The scientific method is alive and well.
Never mind the frequency, feel the width
So far, all we’ve managed is to document here is what we don’t know for sure yet. But we do know there is extra energy in the system now, so could it have any other effects on tropical storms? Here, the science is far less equivocal, and there is a broad consensus that storms are increasing in strength, or severity. This attribute, called the Power Dissipation Index, measures the duration and intensity (wind speed) of storms, and research has found that since the mid-1970s, there has been an increase in the energy of storms.
Recent research has shown that we are experiencing more storms with higher wind speeds, and these storms will be more destructive, last longer and make landfall more frequently than in the past. Because this phenomenon is strongly associated with sea surface temperatures, it is reasonable to suggest a strong probability that the increase in storm intensity and climate change are linked.
This post is the Basic version (written by Graham Wayne) of the skeptic argument "Hurricanes aren't linked to global warming".































 Arguments
Arguments
























 0
0  0
0






Comments