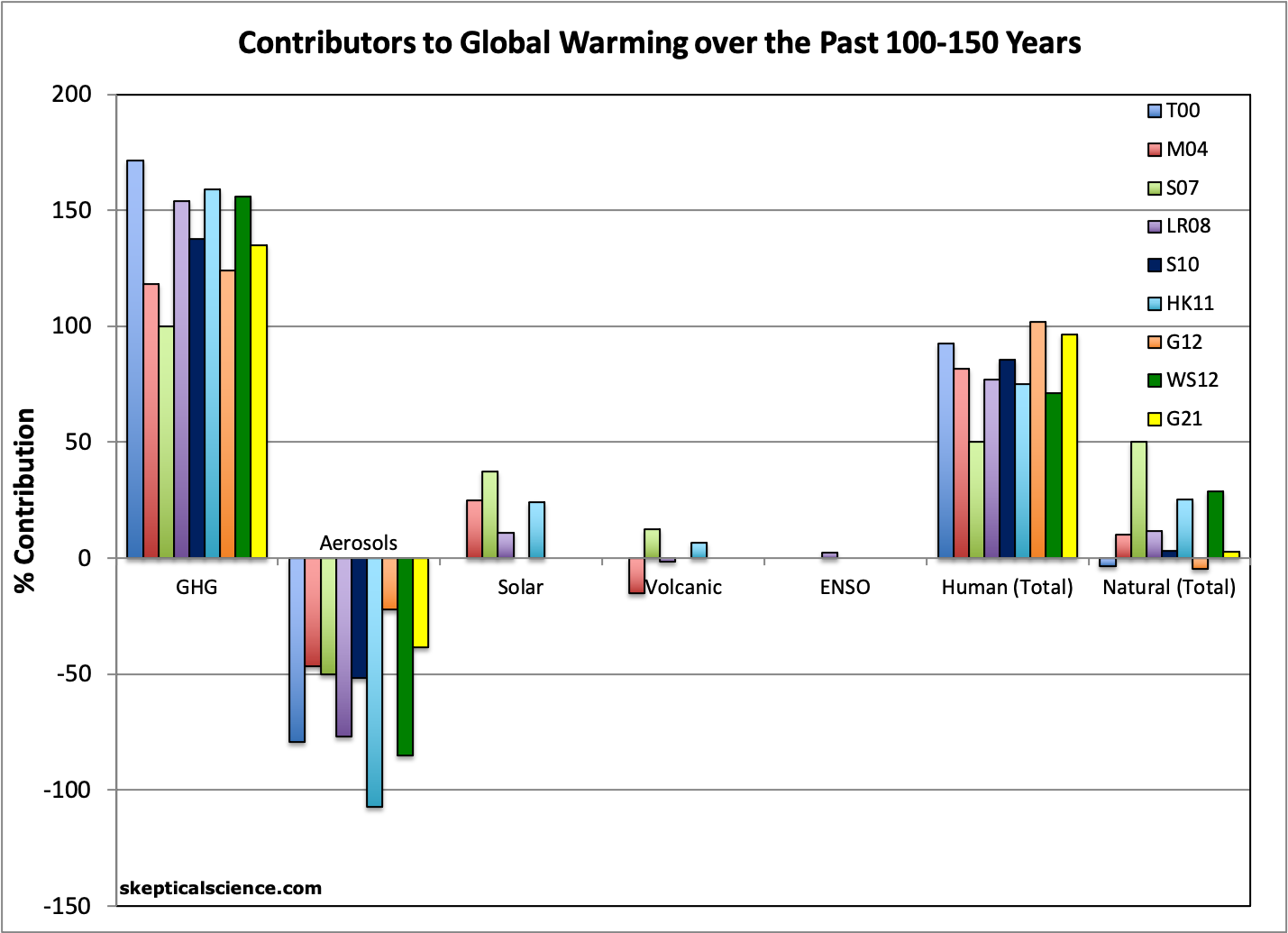
The Human vs. Natural Contributions to Global Warming chart on the Skeptical Science Graphics Page has been updated to include the study discussed below
A new study published in Nature Climate Change, Gillett et al. (2021), is the latest in a long line of 'detection and attribution' studies published over the past 20-plus years that have sought to quantify the factors responsible for the rise in average global surface temperatures.
Gillett et al. used Detection and Attribution Model Intercomparison Project simulations from 13 Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) models. The authors note that the CMIP6 historical simulations "show very little net anthropogenic warming before the 1960s. This contrasts with the CMIP5 historical simulations, which showed on average approximately 0.2°C warming by the mid-twentieth century."
To determine the attribution of the observed global surface warming of 1.1°C between the late 19th Century and the past decade, the authors performed a variant of linear regression – an optimal detection analysis using a regularized optimal fingerprinting algorithm. They conclude:
"anthropogenic forcings caused 0.9 to 1.3°C of warming in global mean near-surface air temperature in 2010–2019 relative to 1850–1900, compared with an observed warming of 1.1°C. Greenhouse gases and aerosols contributed changes of 1.2 to 1.9°C and −0.7 to −0.1°C, respectively, and natural forcings contributed negligibly. These results demonstrate the substantial human influence on climate so far and the urgency of action needed to meet the Paris Agreement goals."
In short, humans are responsible for close to 100% of global surface warming over the past 150 years. Specifically, based on their central attribution estimates, greenhouse gases are responsible for about 1.54°C (135%) of the warming, offset by 0.44°C cooling from aerosols (-38%), plus around 0.03°C warming from natural effects (3%). The Gillett et al. (2021) results are illustrated by the yellow bars in the charts below (note that they didn't break out the various [solar/volcanic/ENSO] natural factors in this study, as some others have).

Factors attributed to causing average global surface warming since the late 19th Century by various studies, including Tett et al. 2000 (T00, dark blue), Meehl et al. 2004 (M04, red), Stone et al. 2007 (S07, light green), Lean and Rind 2008 (LR08, purple), Huber and Knutti 2011 (HK11, light blue), Gillett et al. 2012 (G12, orange), Wigley and Santer 2012 (WG12, dark green), and Gillett et al. 2021 (G21, yellow).
Looking at the warming since the mid-20th Century (close to 0.9°C), we see a similar story: warming from greenhouse gases of about 1.1°C (125%), offset by around 0.2°C cooling from aerosols (-25%), and essentially no net temperature influence from natural factors.
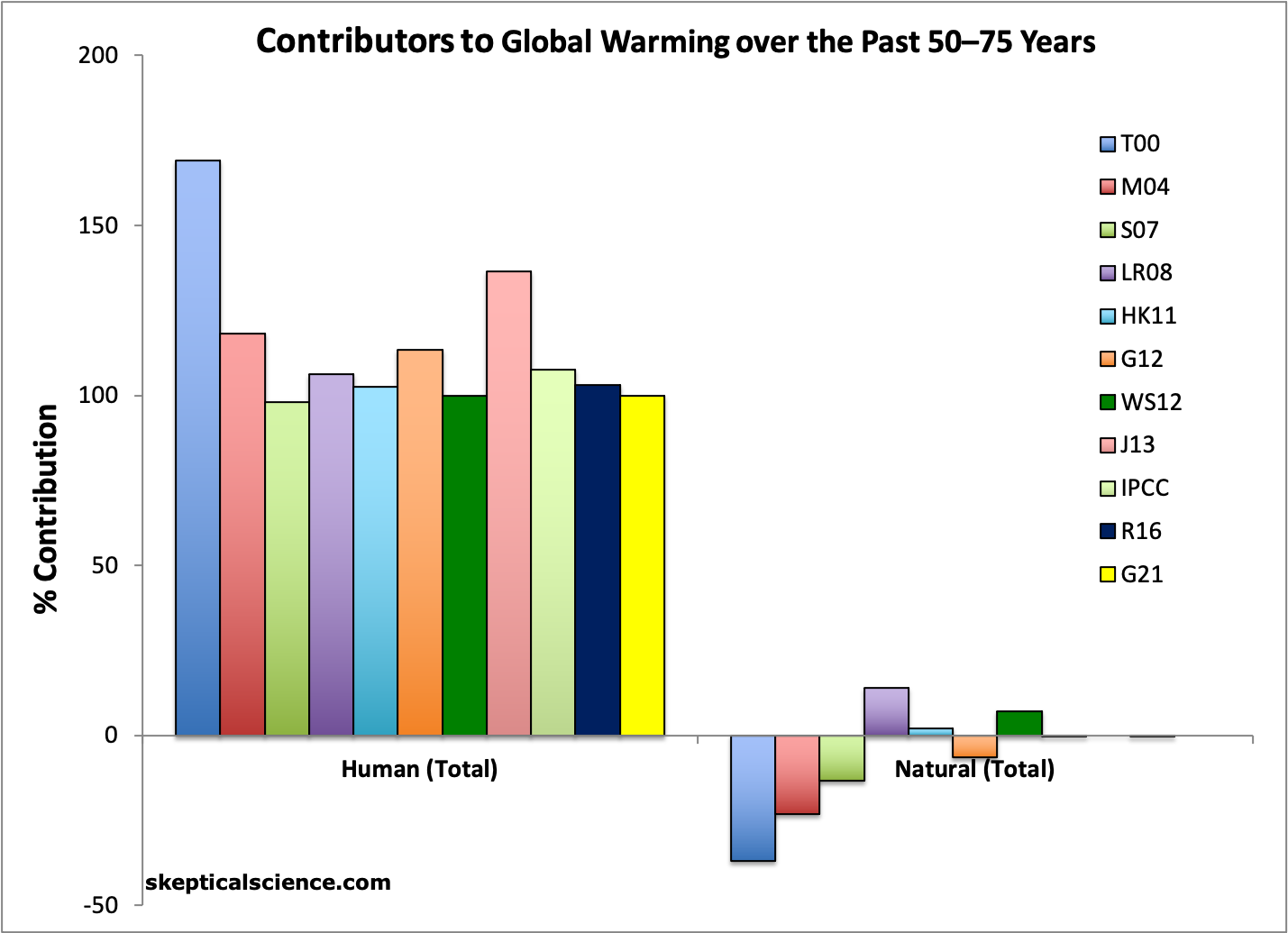
Factors attributed to causing average global surface warming since the mid-20th Century by various studies, including Tett et al. 2000 (T00, dark blue), Meehl et al. 2004 (M04, red), Stone et al. 2007 (S07, green), Lean and Rind 2008 (LR08, purple), Huber and Knutti 2011 (HK11, light blue), Gillett et al. 2012 (G12, orange), Wigley and Santer 2012 (WG12, dark green), Jones et al. 2013 (J13, pink), IPCC AR5 (IPCC, light green), Ribes et al. 2016 (R16, dark blue), and Gillett et al. 2021 (G21, yellow).
The studies paint a consistent picture – human fossil fuel pollution is responsible for all of the global warming since 1950, and if Gillett et al. (2021) are correct, potentially all of the warming since the Industrial Revolution.
Posted by dana1981 on Tuesday, 19 January, 2021
 |
The Skeptical Science website by Skeptical Science is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. |